Websearch
Websearch is the capability to browse the web in search of information, this tool does not only fix the limitations of models of not being up to date due to their training data, but also allows them to actually retrieve recent information or access specific websites.
A handy tool for any agent that needs to be up to date with the world.
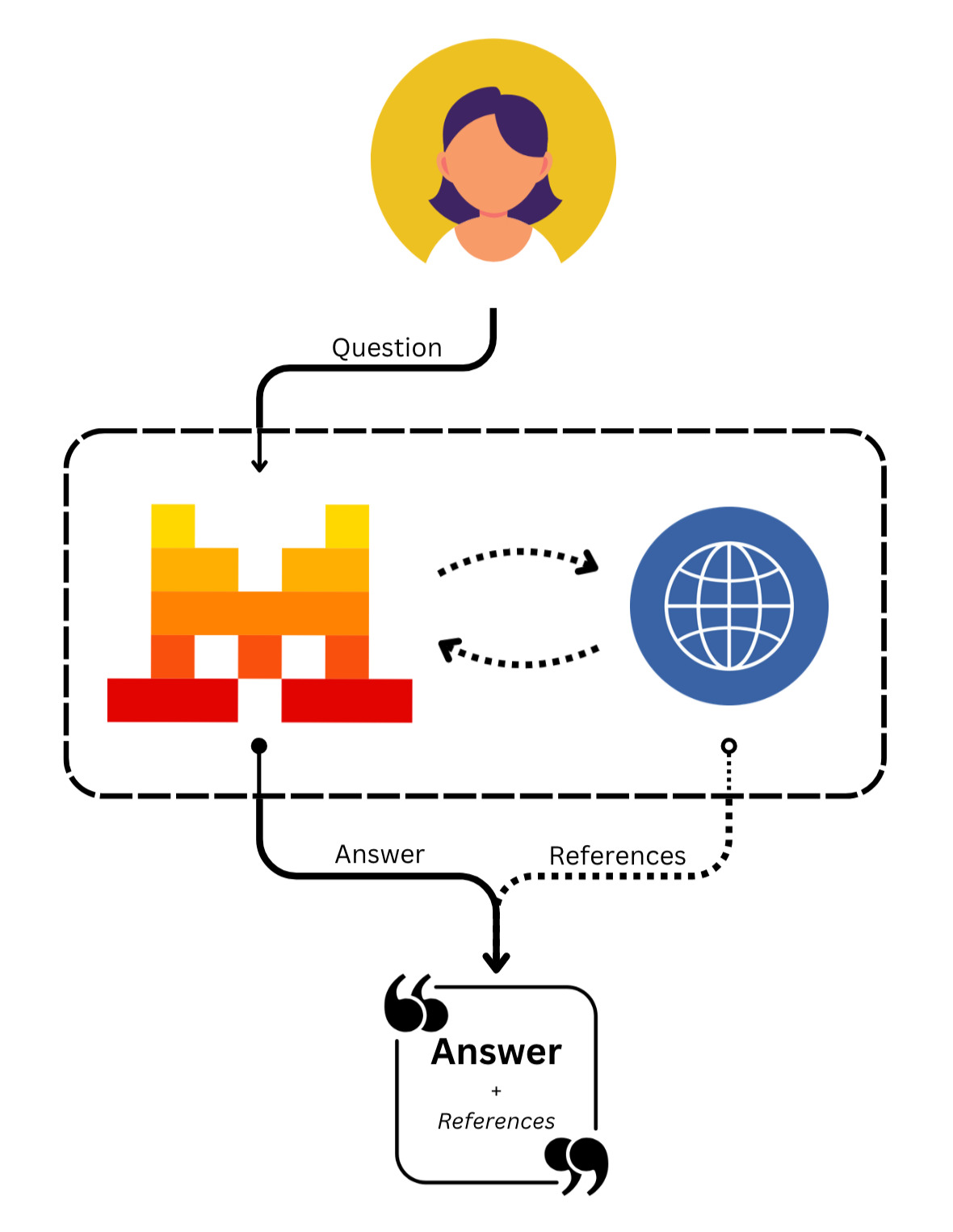
Our built-in tool tool for websearch allows any of our models to access the web at any point to search websites and sources for relevant information to answer the given query.
There are two versions:
web_search: A simple web search tool that enables access to a search engine.web_search_premium: A more complex web search tool that enables access to both a search engine and to news articles via integrated news provider verification.
Create a Websearch Agent
You can create an agent with access to websearch by providing it as one of the tools.
Note that you can still add more tools to the agent, the model is free to search the web or not on demand.
websearch_agent = client.beta.agents.create(
model="mistral-medium-latest",
description="Agent able to search information over the web, such as news, weather, sport results...",
name="Websearch Agent",
instructions="You have the ability to perform web searches with `web_search` to find up-to-date information.",
tools=[{"type": "web_search"}],
completion_args={
"temperature": 0.3,
"top_p": 0.95,
}
)As for other agents, when creating one you will receive an agent id corresponding to the created agent that you can use to start a conversation.
How it Works
Now that we have our websearch agent ready, we can at any point make use of it to ask it questions about recent events.
Conversations with Websearch
To start a conversation with our websearch agent, we can use the following code:
response = client.beta.conversations.start(
agent_id=websearch_agent.id,
inputs="Who won the last European Football cup?"
)Explanation of the Output
Below we will explain the different outputs of the response of the previous snippet example:
-
tool.execution: This entry corresponds to the execution of the web search tool. It includes metadata about the execution, such as:name: The name of the tool, which in this case isweb_search.object: The type of object, which isentry.type: The type of entry, which istool.execution.created_atandcompleted_at: Timestamps indicating when the tool execution started and finished.id: A unique identifier for the tool execution.
-
message.output: This entry corresponds to the generated answer from our agent. It includes metadata about the message, such as:content: The actual content of the message, which in this case is a list of chunks. These chunks correspond to the text chunks, the actual message response of the model, interleaved with reference chunks. These reference chunks are used for citations during Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) related tool usages. In this case, it provides the source of the information it just answered with, which is extremely useful for web search. This allows for transparent feedback on where the model got its response from for each section and fact answered with. Thecontentsection includes:type: The type of chunk, which can betextortool_reference.text: The actual text content of the message.tool: The name of the tool used for the reference, which in this case isweb_search.title: The title of the reference source.url: The URL of the reference source.source: The source of the reference.
object: The type of object, which isentry.type: The type of entry, which ismessage.output.created_atandcompleted_at: Timestamps indicating when the message was created and completed.id: A unique identifier for the message.agent_id: A unique identifier for the agent that generated the message.model: The model used to generate the message, which in this case ismistral-medium-latest.role: The role of the message, which isassistant.
More
Another tool that pro-actively uses references is the document library tool, feel free to take a look here.
For more information regarding the use of citations, you can find more here.