Coding
LLMs are powerfull tools for text generation, and they also show great performance in code generation for multiple tasks, both for code completion, code generation and agentic tool use for semi-automated software development.
We provide 2 major families of llms for coding:
- Codestral: Specifically trained for Code Generation and FIM.
- Devstral: Specifically trained for Agentic Tool Use for Software Development.
Note that we also provide Codestral Embed, for semantic search and embedding code databases, repositories, and powering coding assistants with state-of-the-art retrieval. Learn more about it here.
Before You Start
Endpoints & Models
We provide 2 main endpoints:
- Fill-In-The-Middle :
https://api.mistral.ai/v1/fim/completions- for code completion and code generation; supporting
codestral-latest.
- for code completion and code generation; supporting
- Instruction Following:
https://api.mistral.ai/v1/chat/completions- for coding and agentic tool use; supporting
codestral-latest,devstral-small-latestanddevstral-medium-latest.
- for coding and agentic tool use; supporting
FIM and IF
Use Coding specialized Models
Below you can find how to use our coding dedicated models, from code completion to instruction following and agentic models.
With this feature, users can define the starting point of the code using a prompt, and the ending point of the code using an optional suffix and an optional stop. The FIM model will then generate the code that fits in between, making it ideal for tasks that require a specific piece of code to be generated.
We also provide the min_tokens and max_tokens sampling parameters, which are particularly useful for code generation as it allows you to set the minimum and maximum number of tokens that should be produced. This is especially useful when FIM models decide to produce no tokens at all, or are overly verbose, allowing developers to enforce completions within a specific range if they are needed.
Codestral
Codestral is a cutting-edge generative model that has been specifically designed and optimized for code generation tasks, including fill-in-the-middle and code completion. Codestral was trained on 80+ programming languages, enabling it to perform well on both common and less common languages.
We currently offer two domains for Codestral endpoints, both providing FIM and instruct routes:
| Domain | Features |
|---|---|
| codestral.mistral.ai | - Monthly subscription based, currently free to use - Requires a new key for which a phone number is needed |
| api.mistral.ai | - Allows you to use your existing API key and you can pay to use Codestral - Ideal for business use |
Wondering which endpoint to use?
- If you're a user, wanting to query Codestral as part of an IDE plugin, codestral.mistral.ai is recommended.
- If you're building a plugin, or anything that exposes these endpoints directly to the user, and expect them to bring their own API keys, you should also target codestral.mistral.ai
- For all other use cases, api.mistral.ai will be better suited
This guide uses api.mistral.ai for demonstration.
Below we present three approaches to using Codestral for code generation.
Originally, these models are designed to complete code in-between 2 points: a prefix (here called prompt) and a suffix, generating the code in-between.
import os
from mistralai import Mistral
api_key = os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"]
client = Mistral(api_key=api_key)
model = "codestral-latest"
prompt = "def fibonacci(n: int):"
suffix = "n = int(input('Enter a number: '))\nprint(fibonacci(n))"
response = client.fim.complete(
model=model,
prompt=prompt,
suffix=suffix,
temperature=0,
# min_tokens=1, # Uncomment to enforce completions to at least 1 token
)The prefix + completion + suffix will correspond to the full code.
# prefix
def fibonacci(n: int):
# completion
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
# suffix
n = int(input('Enter a number: '))
print(fibonacci(n))Integrations
Integrations using our Models
If you are interested on leveraging our models in your favorite IDE, you can find below a list of integrations.
Mistral Vibe
Mistral Vibe is a command-line coding assistant powered by Mistral's models. It provides a conversational interface to your codebase, allowing you to use natural language to explore, modify, and interact with your projects through a powerful set of tools.
You can find more information about it here or access the github repository here.
More
Integration with continue.dev
Continue.dev supports both Codestral base for code generation and Codestral Instruct for chat.
How to set up Codestral with Continue
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to set up Codestral with Continue using the Mistral AI API:
-
Install the Continue VS Code or JetBrains extension following the instructions here. Please make sure you install Continue version >v0.8.33.
-
Automatic set up:
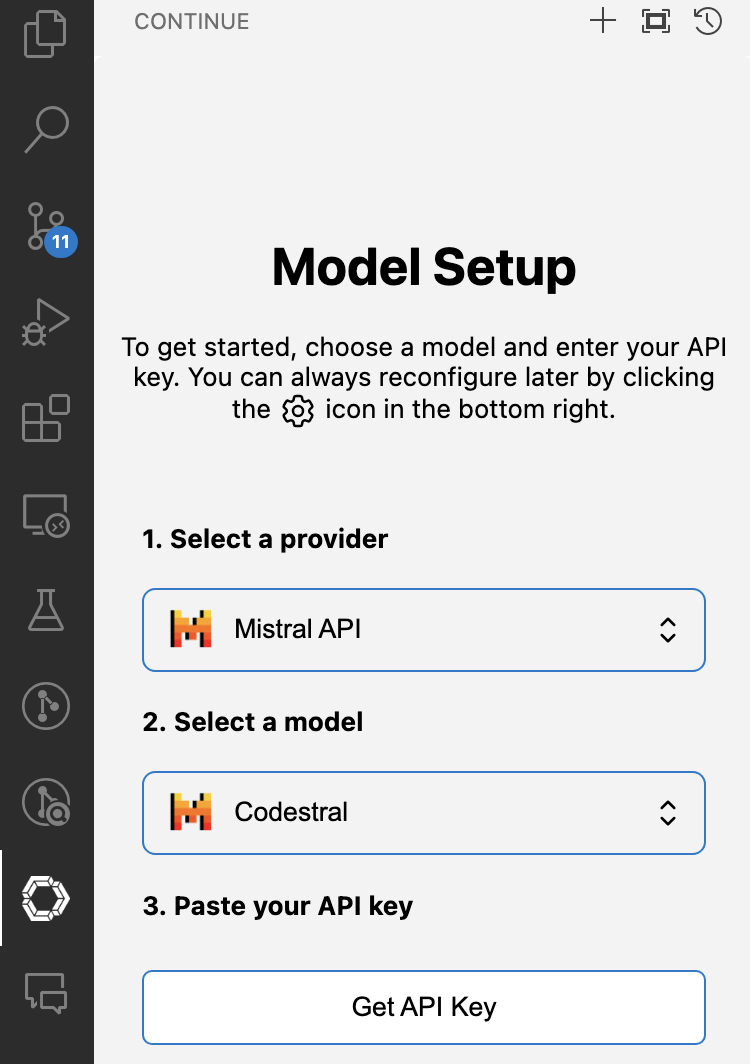
- Click on the Continue extension iron on the left menu. Select
Mistral APIas a provider, selectCodestralas a model. - Click "Get API Key" to get Codestral API key.
- Click "Add model", which will automatically populate the config.json.
- (alternative) Manually edit config.json
- Click on the gear icon in the bottom right corner of the Continue window to open
~/.continue/config.json(MacOS) /%userprofile%\.continue\config.json(Windows) - Log in and request a Codestral API key on Mistral AI's La Plateforme here
- To use Codestral as your model for both
autocompleteandchat, replace[API_KEY]with your Mistral API key below and add it to yourconfig.jsonfile:
{
"models": [
{
"title": "Codestral",
"provider": "mistral",
"model": "codestral-latest",
"apiKey": "[API_KEY]"
}
],
"tabAutocompleteModel": {
"title": "Codestral",
"provider": "mistral",
"model": "codestral-latest",
"apiKey": "[API_KEY]"
}
}If you run into any issues or have any questions, please join our Discord and post in #help channel here
Integration with Tabnine
Tabnine supports Codestral Instruct for chat.
How to set up Codestral with Tabnine
What is Tabnine Chat?
Tabnine Chat is a code-centric chat application that runs in the IDE and allows developers to interact with Tabnine’s AI models in a flexible, free-form way, using natural language. Tabnine Chat also supports dedicated quick actions that use predefined prompts optimized for specific use cases.
Getting started
To start using Tabnine Chat, first launch it in your IDE (VSCode, JetBrains, or Eclipse). Then, learn how to interact with Tabnine Chat, for example, how to ask questions or give instructions. Once you receive your response, you can read, review, and apply it within your code.
Selecting Codestral as Tabnine Chat App model
In the Tabnine Chat App, use the model selector to choose Codestral.
Integration with LangChain
LangChain provides support for Codestral Instruct. Here is how you can use it in LangChain:
# make sure to install `langchain` and `langchain-mistralai` in your Python environment
import os
from langchain_mistralai import ChatMistralAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
api_key = os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"]
mistral_model = "codestral-latest"
llm = ChatMistralAI(model=mistral_model, temperature=0, api_key=api_key)
llm.invoke([("user", "Write a function for fibonacci")])For a more complex use case of self-corrective code generation using the instruct Codestral tool use, check out this notebook and this video:
Integration with LlamaIndex
LlamaIndex provides support for Codestral Instruct and Fill In Middle (FIM) endpoints. Here is how you can use it in LlamaIndex:
# make sure to install `llama-index` and `llama-index-llms-mistralai` in your Python enviornment
import os
from llama_index.core.llms import ChatMessage
from llama_index.llms.mistralai import MistralAI
api_key = os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"]
mistral_model = "codestral-latest"
messages = [
ChatMessage(role="user", content="Write a function for fibonacci"),
]
MistralAI(api_key=api_key, model=mistral_model).chat(messages)Check out more details on using Instruct and Fill In Middle(FIM) with LlamaIndex in this notebook.
Integration with Jupyter AI
Jupyter AI seamlessly integrates Codestral into JupyterLab, offering users a streamlined and enhanced AI-assisted coding experience within the Jupyter ecosystem. This integration boosts productivity and optimizes users' overall interaction with Jupyter.
To get started using Codestral and Jupyter AI in JupyterLab, first install needed packages in your Python environment:
pip install jupyterlab langchain-mistralai jupyter-ai pandas matplotlibThen launch Jupyter Lab:
jupyter labAfterwards, you can select Codestral as your model of choice, input your Mistral API key, and start coding with Codestral!
Integration with JupyterLite
JupyterLite is a project that aims to bring the JupyterLab environment to the web browser, allowing users to run Jupyter directly in their browser without the need for a local installation.
Integration with Tabby
Tabby is an open-source AI coding assistant. You can use Codestral for both code completion and chat via Tabby.
To use Codestral in Tabby, configure your model configuration in ~/.tabby/config.toml as follows.
[model.completion.http]
kind = "mistral/completion"
api_endpoint = "https://api.mistral.ai"
api_key = "secret-api-key"You can check out Tabby's documentation to learn more.
Integration with E2B
E2B provides open-source secure sandboxes for AI-generated code execution. With E2B, it is easy for developers to add code interpreting capabilities to AI apps using Codestral.
In the following examples, the AI agent performs a data analysis task on an uploaded CSV file, executes the AI-generated code by Codestral in the sandboxed environment by E2B, and returns a chart, saving it as a PNG file.
Python implementation (cookbook):
JS implementation (cookbook):