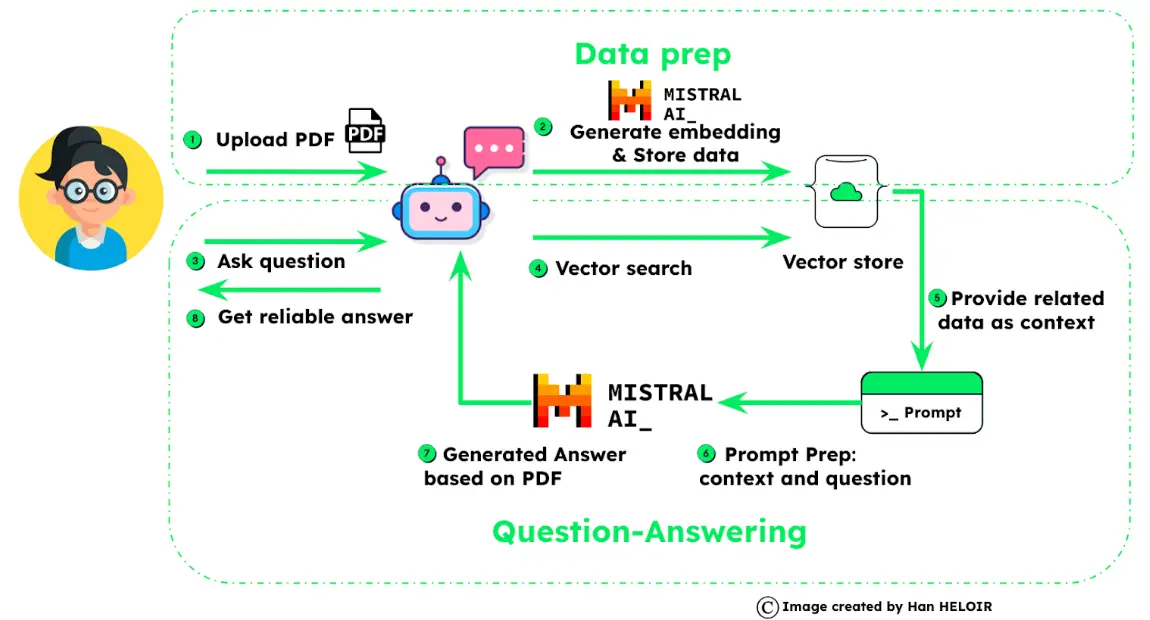
Creating a LLM GenAI application integrates the power of Mistral AI with the robustness of an enterprise-grade vector store like MongoDB. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide to implementing this innovative system:
- Set
MISTRAL_API_KEYand set up Subscription to activate it. - Get
MONGO_URIfrom MongoDB Atlas cluster.
export MONGO_URI="Your_cluster_connection_string"
export MISTRAL_API_KEY="Your_MISTRAL_API_KEY"Import needed libraries
This section shows the versions of the required libraries. Personally, I run my code in VScode. So you need to install the following libraries beforehand. Here is the version at the moment I’m running the following code.
mistralai 0.0.8
pymongo 4.3.3
gradio 4.10.0
gradio_client 0.7.3
langchain 0.0.348
langchain-core 0.0.12
pandas 2.0.3
# Install necessary packages
!pip install mistralai==0.0.8
!pip install pymongo==4.3.3
!pip install gradio==4.10.0
!pip install gradio_client==0.7.3
!pip install langchain==0.0.348
!pip install langchain-core==0.0.12
!pip install pandas==2.0.3These include libraries for data processing, web scraping, AI models, and database interactions.
import gradio as gr
import os
import pymongo
import pandas as pd
from mistralai.client import MistralClient
from mistralai.models.chat_completion import ChatMessage
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
You can use your API keys exported from shell commande.
# Check API keys
import os
mistral_api_key = os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"]
mongo_url = os.environ["MONGO_URI"]Data preparation
The data_prep() function loads data from a PDF, a document, or a specified URL. It extracts text content from a webpage/documentation, removes unwanted elements, and then splits the data into manageable chunks. Once the data is chunked, we use the Mistral AI embedding endpoint to compute embeddings for every chunk and save them in the document. Afterward, each document is added to a MongoDB collection.
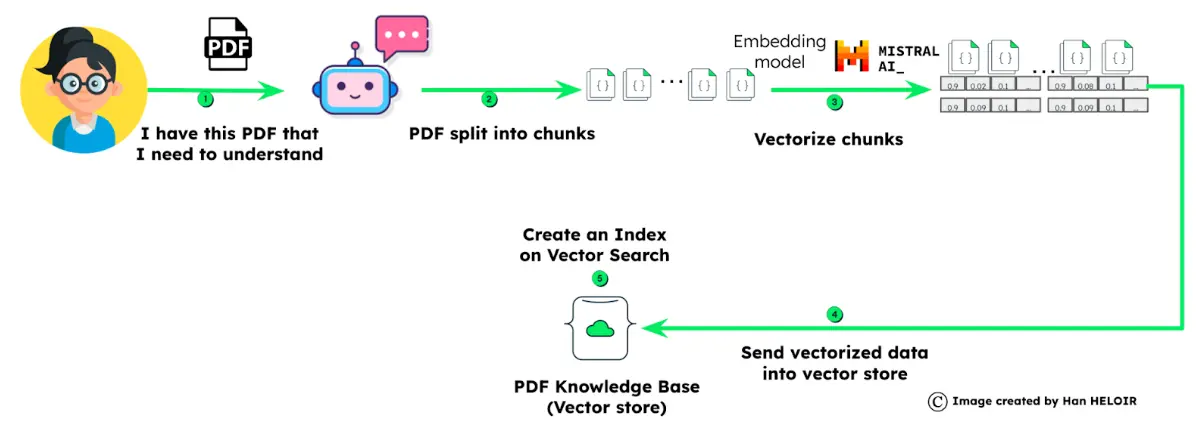
def data_prep(file):
# Set up Mistral client
api_key = os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"]
client = MistralClient(api_key=api_key)
# Process the uploaded file
loader = PyPDFLoader(file.name)
pages = loader.load_and_split()
# Split data
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=100,
chunk_overlap=20,
separators=["\n\n", "\n", "(?<=\. )", " ", ""],
length_function=len,
)
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(pages)
# Calculate embeddings and store into MongoDB
text_chunks = [text.page_content for text in docs]
df = pd.DataFrame({'text_chunks': text_chunks})
df['embedding'] = df.text_chunks.apply(lambda x: get_embedding(x, client))
collection = connect_mongodb()
df_dict = df.to_dict(orient='records')
collection.insert_many(df_dict)
return "PDF processed and data stored in MongoDB."Connecting to MongoDB server
The connect_mongodb() function establishes a connection to a MongoDB server. It returns a collection object that can be used to interact with the database. This function will be called in the data_prep() function.
In order to get your MongoDB connection string, you can go to your MongoDB Atlas console, click the “Connect” button on your cluster, and choose the Python driver.
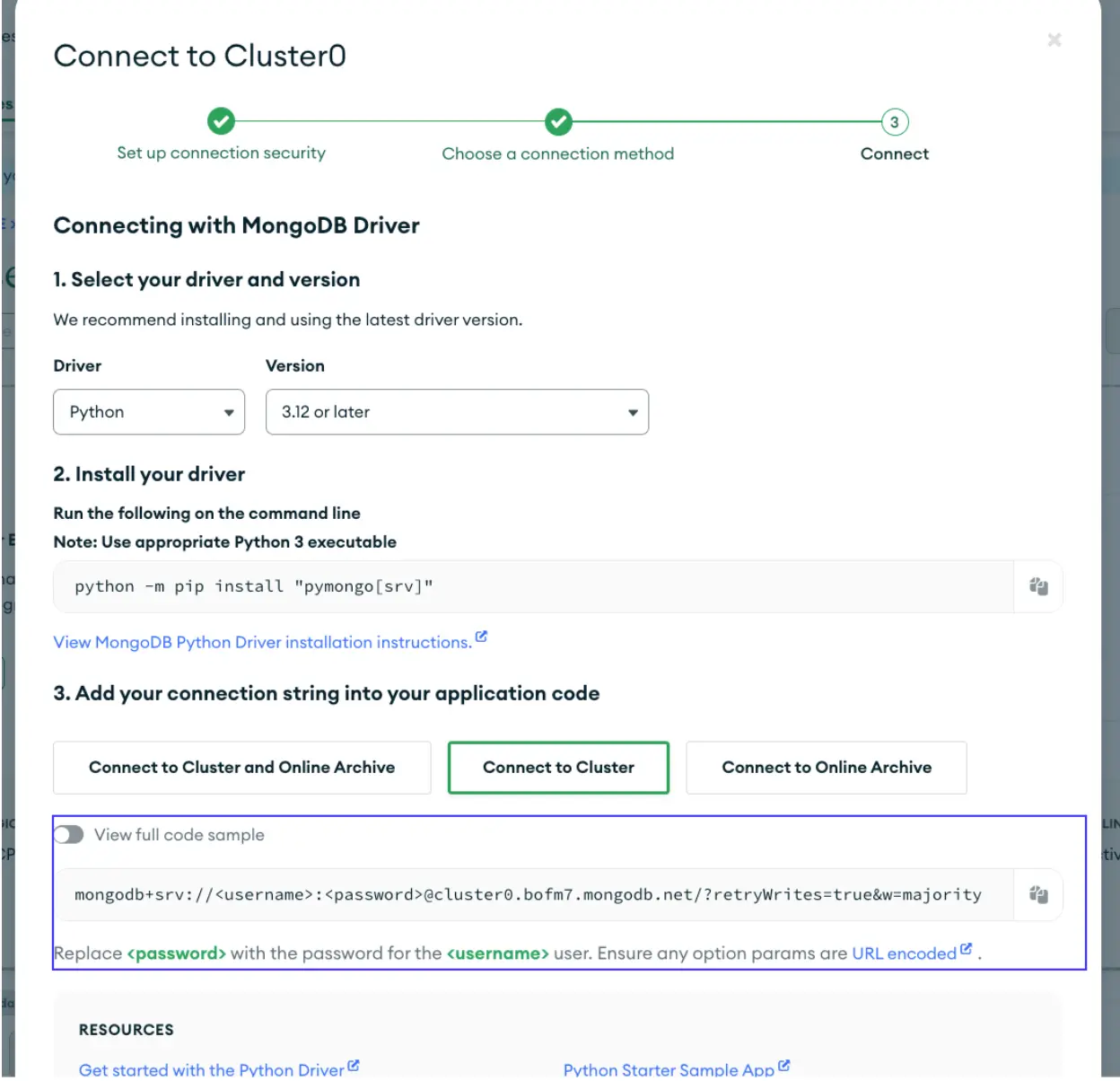
def connect_mongodb(mongo_url):
# Your MongoDB connection string
client = pymongo.MongoClient(mongo_url)
db = client["mistralpdf"]
collection = db["pdfRAG"]
return collectionGetting the embeddings
The get_embedding(text) function generates an embedding for a given text. It replaces newline characters and then uses Mistral AI “La plateforme” embedding endpoints to get the embedding. This function will be called in both data preparation and question and answering processes.
def get_embedding(text, client):
text = text.replace("\n", " ")
embeddings_batch_response = client.embeddings(
model="mistral-embed",
input=text,
)
return embeddings_batch_response.data[0].embeddingThe last configuration on the MongoDB vector search index
In order to run a vector search query, you only need to create a vector search index in MongoDB Atlas as follows. (You can also learn more about how to create a vector search index https://www.mongodb.com/docs/atlas/atlas-vector-search/vector-search-type/ .)
{
"type": "vectorSearch",
"fields": [
{
"numDimensions": 1536,
"path": "'embedding'",
"similarity": "cosine",
"type": "vector"
}
]
}Finding similar documents
The find_similar_documents(embedding) function runs the vector search query in a MongoDB collection. This function will be called when the user asks a question. We will use this function to find similar documents to the questions in the question and answering process.
def find_similar_documents(embedding):
collection = connect_mongodb()
documents = list(
collection.aggregate([
{
"$vectorSearch": {
"index": "vector_index",
"path": "embedding",
"queryVector": embedding,
"numCandidates": 20,
"limit": 10
}
},
{"$project": {"_id": 0, "text_chunks": 1}}
]))
return documentsQuestion and answer function
This function is the core of the program. It processes a user's question and creates a response using the context supplied by Mistral AI.
Question and answer process
This process involves several key steps. Here’s how it works:
Firstly, we generate a numerical representation, called an embedding, through a Mistral AI embedding endpoint, for the user’s question.
Next, we run a vector search in the MongoDB collection to identify the documents similar to the user’s question.
It then constructs a contextual background by combining chunks of text from these similar documents. We prepare an assistant instruction by combining all this information.
The user’s question and the assistant’s instruction are prepared into a prompt for the Mistral AI model.
Finally, Mistral AI will generate responses to the user thanks to the retrieval-augmented generation process.

def qna(users_question):
# Set up Mistral client
api_key = os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"]
client = MistralClient(api_key=api_key)
question_embedding = get_embedding(users_question, client)
print("-----Here is user question------")
print(users_question)
documents = find_similar_documents(question_embedding)
print("-----Retrieved documents------")
print(documents)
for doc in documents:
doc['text_chunks'] = doc['text_chunks'].replace('\n', ' ')
for document in documents:
print(str(document) + "\n")
context = " ".join([doc["text_chunks"] for doc in documents])
template = f"""
You are an expert who loves to help people! Given the following context sections, answer the
question using only the given context. If you are unsure and the answer is not
explicitly written in the documentation, say "Sorry, I don't know how to help with that."
Context sections:
{context}
Question:
{users_question}
Answer:
"""
messages = [ChatMessage(role="user", content=template)]
chat_response = client.chat(
model="mistral-large-latest",
messages=messages,
)
formatted_documents = '\n'.join([doc['text_chunks'] for doc in documents])
return chat_response.choices[0].message, formatted_documents